Several miles above Earth floats the Hubble space telescope with an unparalleled view over the universe, serving its purpose of capturing the mystery hidden in the night sky laced with cosmic objects.
What is a Hubble space telescope?
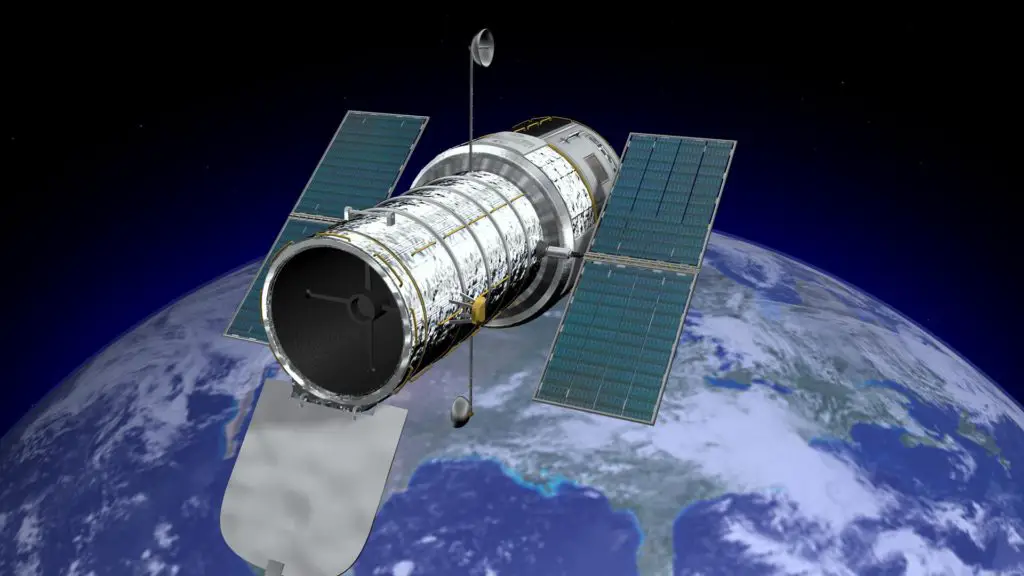 The Hubble Space Telescope is an enormous telescope in space that sends back the right image of the “virtual” sky above for scientists to study and analyze. The advantages of hubble space telescope include the coverage of all cosmic objects with the highest resolution possible, the ability to detect and capture all levels of electromagnetic radiations, and much more.
The Hubble Space Telescope is an enormous telescope in space that sends back the right image of the “virtual” sky above for scientists to study and analyze. The advantages of hubble space telescope include the coverage of all cosmic objects with the highest resolution possible, the ability to detect and capture all levels of electromagnetic radiations, and much more.
Hence, the telescope is a significant tool in the astronomy world. It is in a low-Earth orbit and high location, which allows it to give a tremendous viewpoint for digging into the secrets hidden in our universe. Scroll further to learn about all the advantages of the Hubble Telescope, its purpose, and its mechanism.
- What Is Hubble Space Telescope?
- How is the Hubble Space Telescope different?
- Purpose of Hubble Space Telescope
- Hubble space telescope and its advantages
- How does the Hubble Space Telescope Work?
- Facts about Hubble Space Telescope
- Hubble Space Telescope Orbit
- Does the Hubble Telescope take pictures of earth?
- What is Hubble telescope space shuttle?
- Magnification of Hubble Telescope
- Who Built the Hubble Space Telescope?
- Hubble Space Telescope Distance from Earth
- The Discoveries Made by Hubble
How is the Hubble Space Telescope different?
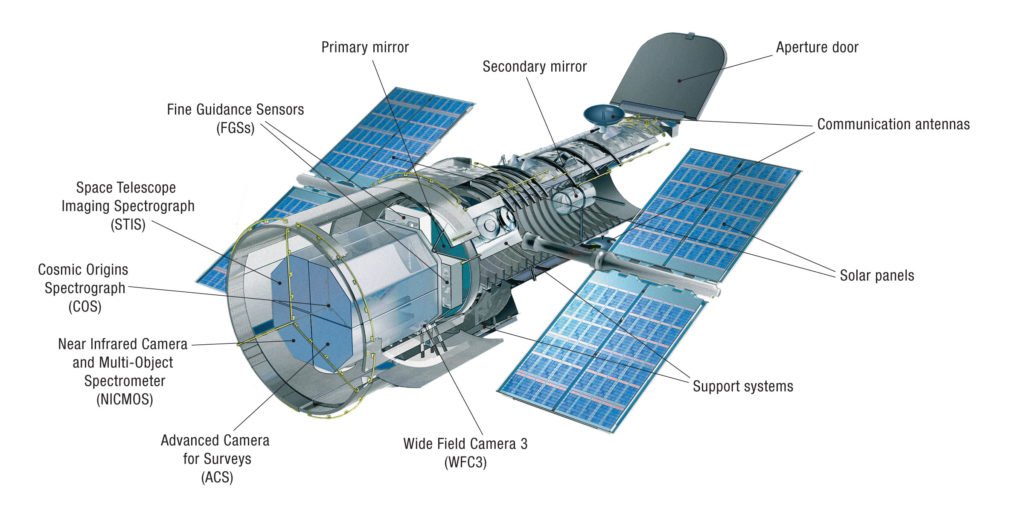
To answer the question of what type of telescope is a Hubble space telescope, we must look into some technical terms. To make it simpler, the Hubble space telescope uses what we call the Cassegrain reflector. Light strikes the telescope’s main mirror or essential mirror. At that point, It skips off the main mirror and experiences a secondary mirror. The essential mirror that notifies the telescope’s science instruments takes the light focused on by a secondary mirror via its focal point pinhole.
Purpose of Hubble Space Telescope
Now to look into the purpose of the Hubble telescope, we must study a brief history in order to grasp the intended purpose of this tool. Hubble Space Telescope was created with a requirement to capture high-resolution images of the universe. It’s capable of taking high-resolution images with irrelevant background light. Though the Hubble space telescope was launched in 1990, the thought of creating this telescope struck the scientists’ path in 1923.
What was established in 1970 had an expected launch in 1980. However, due to some budget constraints, it was officially launched in 1990. Even then, a lingering concern as to which space shuttle would be best suitable to carry the Hubble space telescope into orbit haunted the minds of space experts. What happened next came as a surprise because the primary purpose was not being fulfilled either.
The expected image quality from the first-ever pictures captued and sent back to Earth were not up to the mark. They were neither sharp nor were they of high quality. Upon investigation, an issue that led to this failure was relvealed to be caused by the main mirror shape being grounded incorrectly. Even so, despite the insane cost of the Hubble telescope, it was still considered a major breakthrough for space exploration.
Hubble space telescope and its advantages
The atmosphere of the Earth
Something that really sets the Hubble space telescope apart is its resilience against the atmosphere of the Earth. As well as being able to capture deep-sky objects, it fights against all the issues caused by the levels of atmosphere in outer space. The atmosphere specifically assimilates a few shades of light. Being over the atmosphere permits this information to be gathered.
The detail is totally remarkable
Right when you can wipe out the atmosphere; you have a level of clarity that is still generally unequaled. With the Hubble telescope, you will have the option to capture detail in a genuine manner.
It focuses on the capability of the space program
With all the magneficent pros that came after the development of the telescope, the design did not fall short of some significant disadvantages. The truth of the matter was, however, that it has been more effective than not. If someone neglects to see the requirement for a space program, someone else could highlight the various achievements of the Hubble Space Telescope.
1800s Telescope Black and White

How does the Hubble Space Telescope Work?
Have you ever gazed at the night sky and thought about what the universe resembles very close? Tons of people around the world are compelled to stargaze with simply our eyes, looking for pinpricks of light in the tremendous night. Even if you’re fortunate to approach a earth-based telescope, whose clarity depends on atmospheric factors such as climate and weather, it doesn’t offer the kind of clarity these stunning celestial objects deserve.
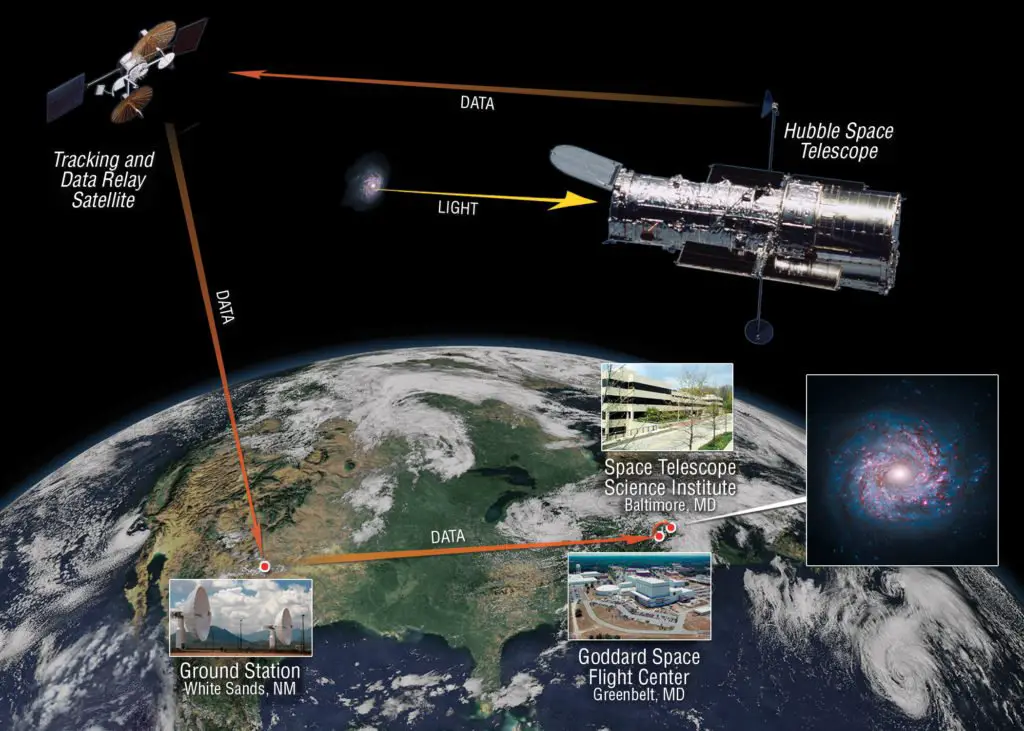
Hubble Space Telescope orbits around Earth, moving at the speed of around five miles for each second (8 km for every second) adequately to cross over the United States in around 10 minutes. As it moves, Hubble’s mirror catches the light and guides it into its few science instruments
At the point when the mirror captures the light, the Hubble’s scientific instruments cooperate or separate to stitch together a perception. Each instrument is intended to break down the universe in an unexpected way.
Facts about Hubble Space Telescope
The Hubble project is a joint task among NASA and the European Space Agency. Some of the key insights regarding the telescope and its main mission were given by the Space Telescope Science Institute. We will also look into the Hubble telescope size and its orbit specifications.
Telescope size:
- Length: 43.5 feet (13.2 meters)
- Weight: 24,500 lbs. (11.11 tons)
- Achieved diameter: 14 feet (168 inches)
Timeline of events for the mission:
- The launch was scheduled for 24th April 1990
- Deployment was planned for 25th April 1990
- Mission 1: Servicing in December 1993
- Mission 2: Servicing in February 1997
- Mission 3A: Servicing in December 1999
- Mission3B: Servicing in February 2002
- Mission 4: Servicing in May 2009
Number regarding its flight in Space and how far is the Hubble space telescope from Earth
- Achieved an average altitude of 569 kilometers at a 28.5 degrees angle to the equator
- Took 97 minutes is the orbital period of Hubble space telescope
- Achieved a speed of 28000 km/h
Important statistics:
All of the data regarding the telescope project would be equal to 3600 feet of books on a rack, and as much as 120 gigabytes in terms of computing data if it were put into perspective. All of this information is stored on Magento-optical disks. Furthermore, all of the Hubble space telescope information that is sent to Earth and its performance is also added to these disks.
Source of power:
- The direct source is the sunlight
- Involves two 25 feet solar panels
- Using 2800 watts of power
- 6 nickel-hydrogen batteries store this energy
Statistics regarding its mirrors:
- The diameter for the primary mirror is 94.5 inches (2.4 m)
- The weight of the primary mirror is 1,825lbs (828 kg)
- The diameter for the secondary mirror is 12 inches (0.3 m)
- The weight of the secondary mirror is 27.4lbs (12.3 kg)
Hubble Space Telescope Orbit
Hubble Space Telescope orbits the Earth at a speed of 27,000 kilometers per hour or 17,000 miles per hour. Its speed when circle above Earth is brisk to the point that any picture it took would be blurred by the ray. At this speed, improvements are being made as to the capacity of detection in telescopes.

Does the Hubble Telescope take pictures of earth?
A blend of gases that encompass the planet are collectively called the atmosphere. Earth’s atmosphere changes prevents some radiations from reaching space. Hubble telescope orbits around and high above the Earth’s atmosphere. Hence, it can capture the space in a much more clear way than most telescopes on Earth can do. Hubble telescope is also not the kind of telescope that you can spot with your bare eyes.
It utilizes an advanced camera to takes pictures, just like how we take pictures through a phone. At that point, it utilizes radio waves energy to forward the photos through the air back to the Earth. This shows us exactly why the Hubble space telescope important for scientific advances in the astronomical field.
What is the Hubble telescope space shuttle?
Hubble telescope space shuttle conveyed individuals into space. The space shuttle performed many tasks beyond the human view. The space shuttle resembled a moving lorry. It carries huge parts into space to assemble the International Space Station. The space shuttle was likewise similar to a science research center.
The astronauts carry out numerous investigations there. Doing experiments in space is unique in relation to Earth’s one. Each time a space shuttle was launched, it was known as a mission. The shuttle was launched for 135 missions’ times and each mission last for one or two weeks. The principal mission was in 1981 while the last mission was in 2011.
Magnification of Hubble Telescope
Most of the inaccessible systems in the universe are typically hidden in the blackout to be seen by earth telescope. Yet, nature has an answer: gravitational lensing anticipated by Albert Einstein and watched commonly by astronomers. Some of the most intriguing instances of gravitational lensing were found by Harald Ebeling at the Institute of Astronomy at the University of Hawaii, Manoa, regarding the general assembling of space expertise.
Utilizing the Hubble Space Telescope to review an example of enormous groups of galaxies, the group found a distant universe, eMACSJ1341 QG 1 that is amplified multiple times because of space-time made by the massive galaxy cluster named eMACSJ1341. 9-2441.
When the hidden physical impact of gravitational lensing was first affirmed during the sun based shroud of 1919, scientists were able significantly amplify pictures of inaccessible divine sources when the adequately massive objects were found to lie between the background source and observers.
Who Built the Hubble Space Telescope?
The Hubble Space Telescope was the principal complex optical observatory put into space around Earth. Ground-based astronomers studied Earth’s atmosphere and developed a perspective of celestial objects by retaining or distorting light rays from them. This telescope was positioned in space over the atmosphere to then attain pictures of a lot more prominent splendor, clearness, and detail than do earth telescopes with equivalent optics.
After the U. S. Congress had approved its development in 1977, Hubble Space Telescope was worked under the oversight of the National Aeronautics and Space Administration of the United States and was named after this astronomy pro Edwin Hubble, the premier American stargazer of the twentieth century
Hubble Space Telescope Distance from Earth
Hubble Space Telescope was put into orbit about 600 km (370 miles) above Earth. The Hubble was shot into orbit on 24th April 1990 as part of the 35th mission for the American Space Shuttle Program also known as STS-31. The lifespan this time is estimated as between 10 to 20 years.
The Discoveries Made by Hubble
Hubble prosperity isn’t just a mere portion as it was placed high over the atmosphere, eliminating numerous impacts that impede earth observers. Indeed, bright astronomy is everything except difficult to finish from the beginning to the presence of gases like ozone that block bright light in the upper environment.
Because of this and the nonattendance of the violent wind currents that cause stars to seem like they are glimmering, Hubble can take presumably the most honed and most profound pictures of our Universe.
At the point when Hubble gives us images in space, the view it gives us is consistent with what objects looked like at some point previously. This is on the grounds that light furher travels to every part of the significant distance from the objects it originated from. For sure, even with generally nearby objects the deferral can be amazing. With our closest neighboring world, the Andromeda universe is now being viewed as it was basically 2.5 million years back
Here is the portion of its significant contributions to science:
- It helped pin down the age for the universe presently known to be 13.8 billion years, around multiple times the time of Earth.
- It helps to discover two moons of Pluto, Nix, and Hydra.
- Also, it helped decide the rate at which the universe is expanding.
- Discovered that essentially every significant galaxy is secured by a dark gap at the center.
- Created a 3-D guide of dark matter
- 10 Best Monocular Telescopes UK in 2022【Reviewed】 - April 1, 2022
- How To Build A Dobsonian Telescope [Guide 2022] - March 31, 2022
- Best Astrophotography Stacking Software [Ultimate Guide] - March 31, 2022
Leave a Reply